
#Palo alto networks vpn nat how to
When the traffic is forced out the interface through the PBF, the traffic will know how to get back to the Secondary VR where the interfaces live. The Primary VR routes include the default route and return routes for all private addresses back to the Secondary VR, where the actual interfaces are as connected routes.Primary VR has Ethernet1/3 interface attached.The purpose is to let all interfaces be known by connected routes and routes on the VR as their routing method when the Main ISP goes down. The policy shown here translates all source addresses with at 10.20.1.x address destined to the Corp Zone to a matching address in the 10.30.1.Each VR has an ISP Interface attached, but all other interfaces will stay connected to VR Secondary, as well as all future interfaces. This is typically used to resolve overlapping IP ranges when merging networks. The number of source IPs using this policy must exactly match the translated range. Use the Static IP mapping type to translate an entire address range to a specific address range, a one-to-one mapping. Static NAT policies for publicly exposed servers usually have Bi-directional set to Yes, so the outbound traffic for the server uses the same address as inbound traffic: If Bi-directional is set to No, then the mapping is created based only on the direction of the source\destination zones. Selecting "Yes" for Bi-directional creates mapping in both directions based on the source\destination zones that are specified. This is typically used to expose a server (email, web or any application) externally using a translated address that will not change. Use this translation type to translate a single source address to a specific public address. To view the current NAT pool mappings for a given NAT policy, run the following CLI command: It is common to assign a range of IP addresses to the dynamic pool: This option is used when there are two or more public IPs from the ISP, but not enough to allocate one to each internal host on the network, and you want to assign them to outbound hosts only as needed. Be aware when using this option, because the translated pool of addresses can be exhausted if the number of internal hosts concurrently creating outbound sessions exceeds the number of IP addresses in the dynamic pool. Each concurrent session uses an address from the pool, making it unavailable to other source IPs.
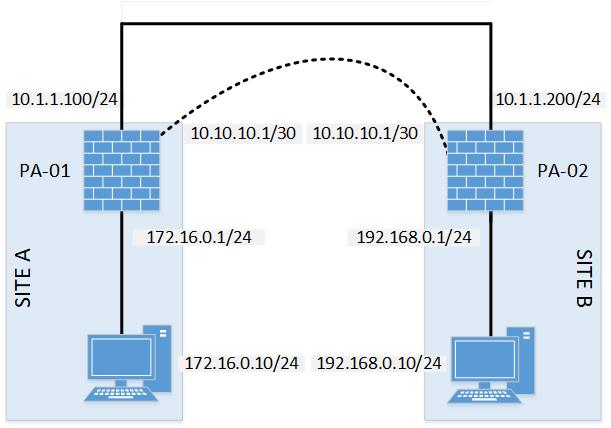
The mapping is not port based, which makes this a one-to-one mapping as long as the session lasts. Use the following CLI command to check the NAT pool utilization: > show running global-ippoolįor a given source IP address, the firewall translates the source IP to an IP in the defined pool or range. The firewall will load balance from the address pool based on each session. To add more IP addresses to the outbound pool, change the address type to "Translated Address" and add a valid public IP to the list. It is common to choose the IP address assigned to the interface connecting to your ISP: This is typical when only having a single public IP address to be shared among many private IP addresses. The mapping is based on source port, so multiple source IPs can share a single translated address until the source ports have been exhausted. Following are available source address translation types and the typical use case for each.įor a given source IP address, the Palo Alto Networks firewall translates the source IP address or range to a single IP address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
